Test and Measurement Tools
In industries like maintenance, plumbing, and electronics, precision is everything — and that’s where test and measurement tools come in. These tools aren’t just helpful; they’re critical to ensuring accuracy, safety, and operational efficiency. Whether it’s verifying complex electronic circuits or inspecting fluid systems, reliable measurement instruments play a vital role across a wide range of technical and industrial environments.
Importance of Test and Measurement Tools
Test and measurement tools are critical for assessing, validating, and monitoring performance across industries like manufacturing, telecom, construction, and electronics. These tools play a central role in troubleshooting, quality control, routine inspections, and ensuring safety compliance.
Key Instruments:
Multimeters:
Essential for measuring voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. Widely used in diagnostics and maintenance, both in analog and digital formats.Oscilloscopes:
Used for advanced electronic diagnostics. They visualize waveform voltages, helping engineers analyze signals and detect faults in real time — especially in telecom, automotive, and aerospace sectors.Pressure Gauges:
Crucial for hydraulic and pneumatic systems, these gauges ensure pressure levels remain within safe and optimal ranges. Available in digital and analog versions.Thermometers:
From HVAC systems to industrial processing, accurate temperature monitoring is vital. Infrared and contact thermometers help maintain efficiency, safety, and product integrity.
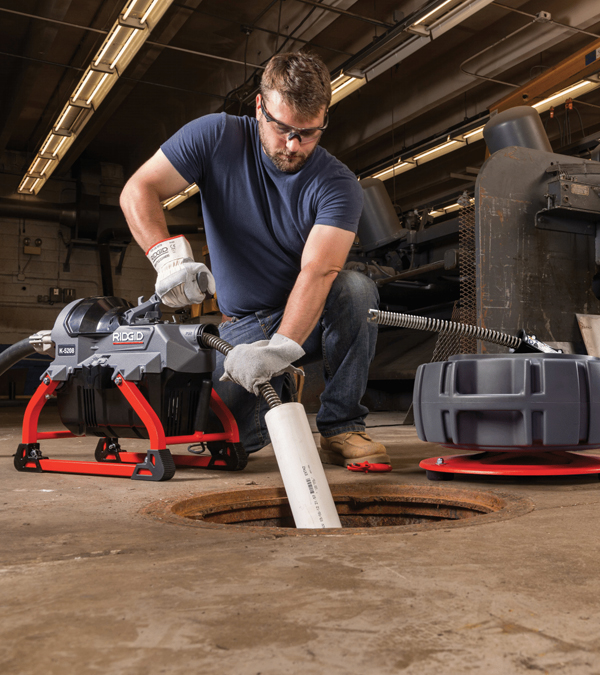


Specialized Tools for Specific Applications
In addition to general-purpose instruments, certain tools are engineered to meet the demands of specific industries:
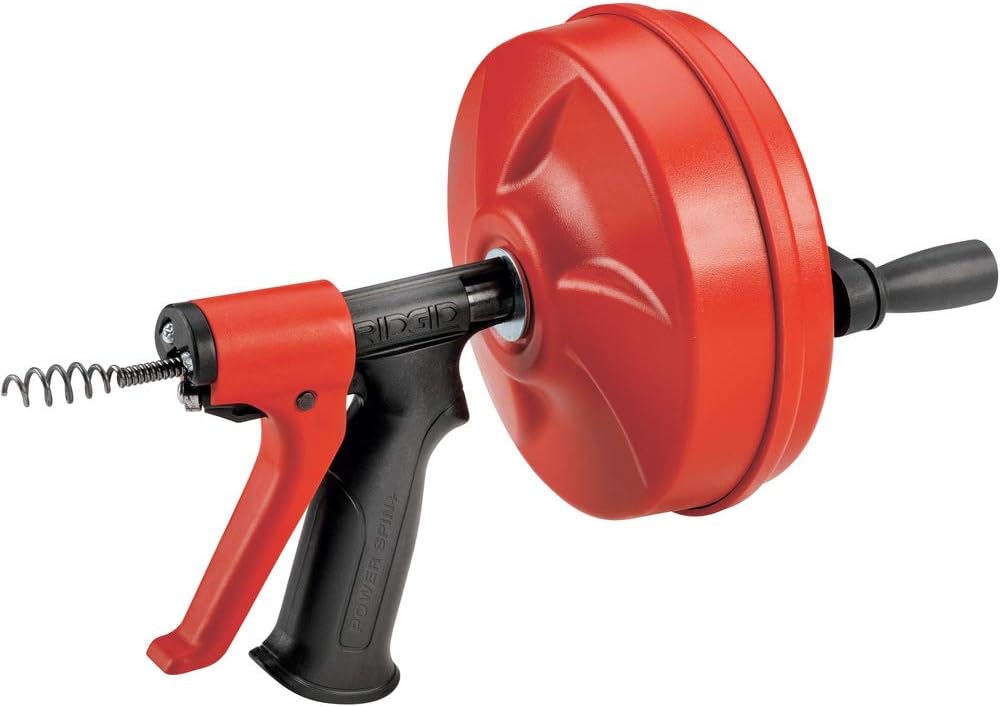
Drain Opener/Cleaner:
Essential in plumbing and wastewater systems, these tools clear blockages using chemical or mechanical methods. They help maintain proper flow, prevent backups, and support sanitary conditions.Copper Press Tools:
Widely used in modern plumbing, copper press tools securely crimp fittings onto copper pipes using hydraulic force. They offer a faster, cleaner, and more reliable alternative to soldering, ensuring leak-proof connections in both residential and commercial applications.
Advancements in Test and Measurement Technology
Modern test and measurement tools have evolved significantly, driven by advancements in connectivity, data processing, and design:
Wireless Connectivity:
Many tools now feature Bluetooth or Wi-Fi capabilities, allowing remote monitoring and real-time data logging—ideal for industrial automation and IoT-driven maintenance systems.Integrated Data Analysis:
Advanced instruments come with built-in software for trend analysis, graphical data visualization, and automated reporting, helping engineers make faster, data-driven decisions.Portable & Durable Design:
Today’s tools are built for mobility and resilience, with compact, rugged casings that ensure reliable performance in field conditions and demanding industrial environments.
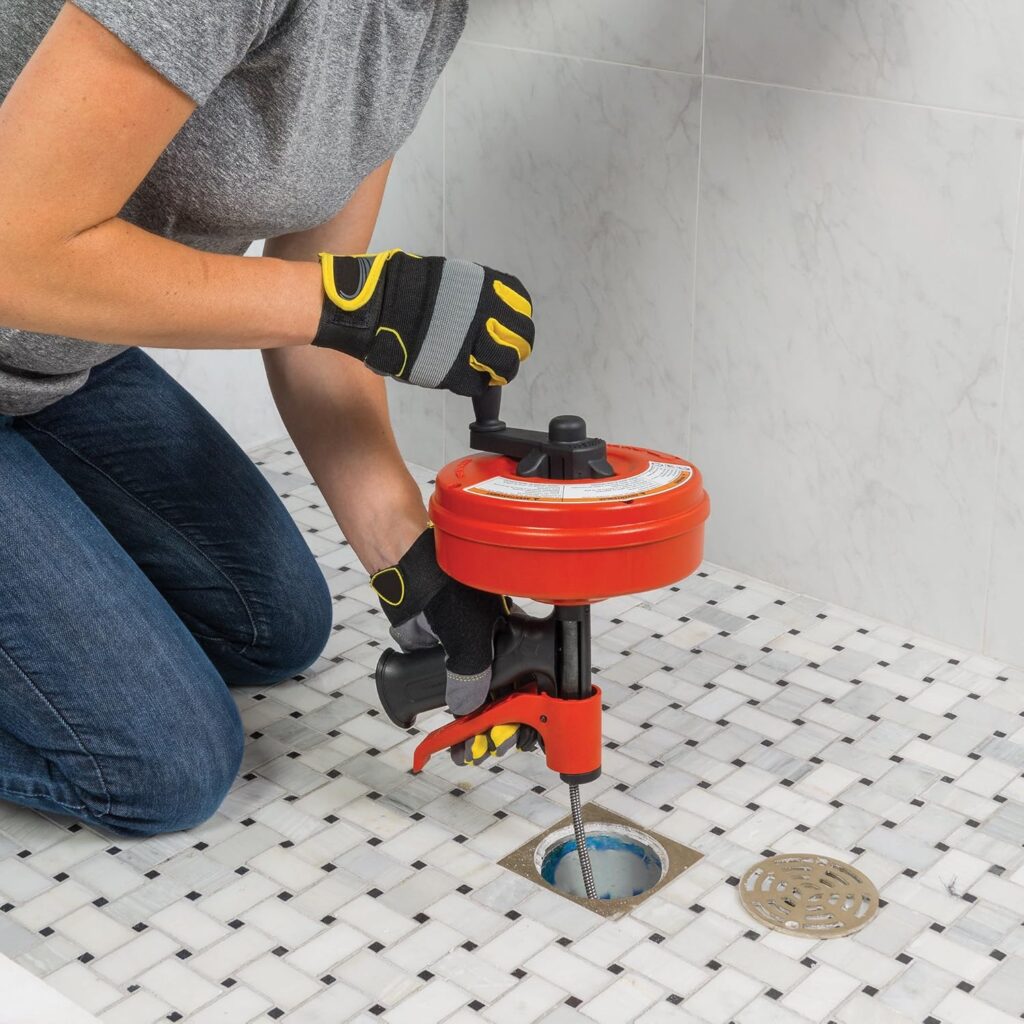


Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries require specialized tools tailored to their operational standards and safety demands:
Automotive Industry:
Technicians use multimeters, oscilloscopes, and vehicle-specific diagnostic tools to troubleshoot electrical systems, monitor engine performance, and ensure compliance with modern automotive electronics.Aerospace & Defense:
High-precision tools like laser alignment systems and vibration analyzers are essential for maintaining aircraft integrity, supporting strict quality control and safety regulations.Energy Sector:
Utilities rely on power quality analyzers, thermal imaging cameras, and insulation testers to monitor grid health, identify faults proactively, and maintain consistent energy delivery.
Future Trends and Innovations
The test and measurement industry is rapidly evolving with a focus on smarter, more sustainable technologies. IoT integration is enabling remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance through real-time data sharing. AI and machine learning are enhancing tool intelligence, allowing for advanced anomaly detection and predictive analytics. Meanwhile, sustainability initiatives are driving the development of energy-efficient, eco-friendly instruments that reduce environmental impact without compromising on precision or performance.


Conclusion
Test and measurement tools are essential for ensuring safety, accuracy, and efficiency across industries. From multimeters to copper press tools, each plays a vital role in maintaining systems and equipment. As technology evolves, these tools are becoming smarter, more connected, and more durable—helping professionals streamline operations and stay ahead in a fast-changing industrial landscape.
Join Us in Shaping the Future of Mining!
Subscribe For Newsletter!